Anatomical Waste Management? Secure Waste Shares: A Step-by-Step Guide
Anatomical waste management: What is it? Is it the same as pathological waste? How is anatomical waste treated and disposed of compared to regular medical waste, such as sharps? Secure Waste is also curious about anatomical waste, so let’s explore this topic together and clarify our understanding.
Anatomical waste refers to human tissues, organs, and body parts that result from surgeries, autopsies, or other medical procedures. It is distinct from pathological waste, typically consisting of biopsies and other specimens that may contain infectious agents but do not include whole body parts.
The treatment and disposal of anatomical waste require specific procedures due to the potential health risks involved. This type of waste is typically incinerated in specialized facilities designed to handle medical waste, ensuring destruction of any harmful pathogens. In contrast, regular medical waste might be disposed of through autoclaving or chemical disinfection before disposal in landfills, mainly if it is classified as non-hazardous.
Sharps, such as needles and surgical blades, also require specialized disposal methods, involving puncture-resistant containers that are then processed through incineration or other approved means to prevent injury or infection.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for healthcare facilities to maintain compliance with safety regulations and protect public health. Let’s delve deeper into each category to enhance our comprehension of effective waste management practices.
Anatomical waste refers to human or animal body parts, tissues, organs, and other biological materials removed during various medical procedures, surgeries, or autopsies. As a specific type of biomedical or clinical waste, anatomical waste requires meticulous handling and disposal due to its potential to transmit infections and pose health risks.
Now let’s Take A Deep Dive Into Every Level Of Anatomical Waste.
Key Characteristics of Anatomical Waste:
- Origin: Anatomical waste is derived from several medical sources, including surgical procedures, biopsies, autopsies, and other research activities involving humans or animals. These sources range from hospitals, clinics, and laboratories to veterinary practices.
- Composition: The composition of anatomical waste can be pretty diverse, consisting of body parts (such as limbs or organs), tissues (such as tumors or biopsied samples), blood and blood products, placentas or umbilical cords from childbirth, and pathological specimens, which may include biopsies and tissues sent for diagnostic analysis. Materials soaked with blood or other bodily fluids, like surgical drapes, sponges, and gauze, are also included in this category.
- Infectious Potential: Anatomical waste is often considered potentially infectious due to its biological nature. This characteristic necessitates stringent protocols for handling and disposal to mitigate the risk of disease transmission. It is common for anatomical waste to harbor pathogens that can lead to infections if not managed appropriately.
- Distinction from Other Waste: While anatomical waste is classified as biomedical waste, it differs significantly from other categories such as sharps (needles, scalpels), pharmaceutical waste (expired or unused medications), or contaminated personal protective equipment (PPE). Each category requires distinct handling and disposal techniques to ensure safety and compliance with health regulations.
Examples of Anatomical Waste:
- Human or animal tissues and organs removed during surgical interventions or autopsies.
- Surgical specimens for diagnostic purposes, including tumor resection samples.
- Blood and blood products, including whole blood or plasma.
- Placentas and other tissues associated with childbirth.
- Severed limbs or body parts resulting from trauma or surgery.
- Pathological specimens are explored in laboratories to diagnose diseases.
- Materials such as gauze, sponges, or cloths saturated with blood or bodily fluids.
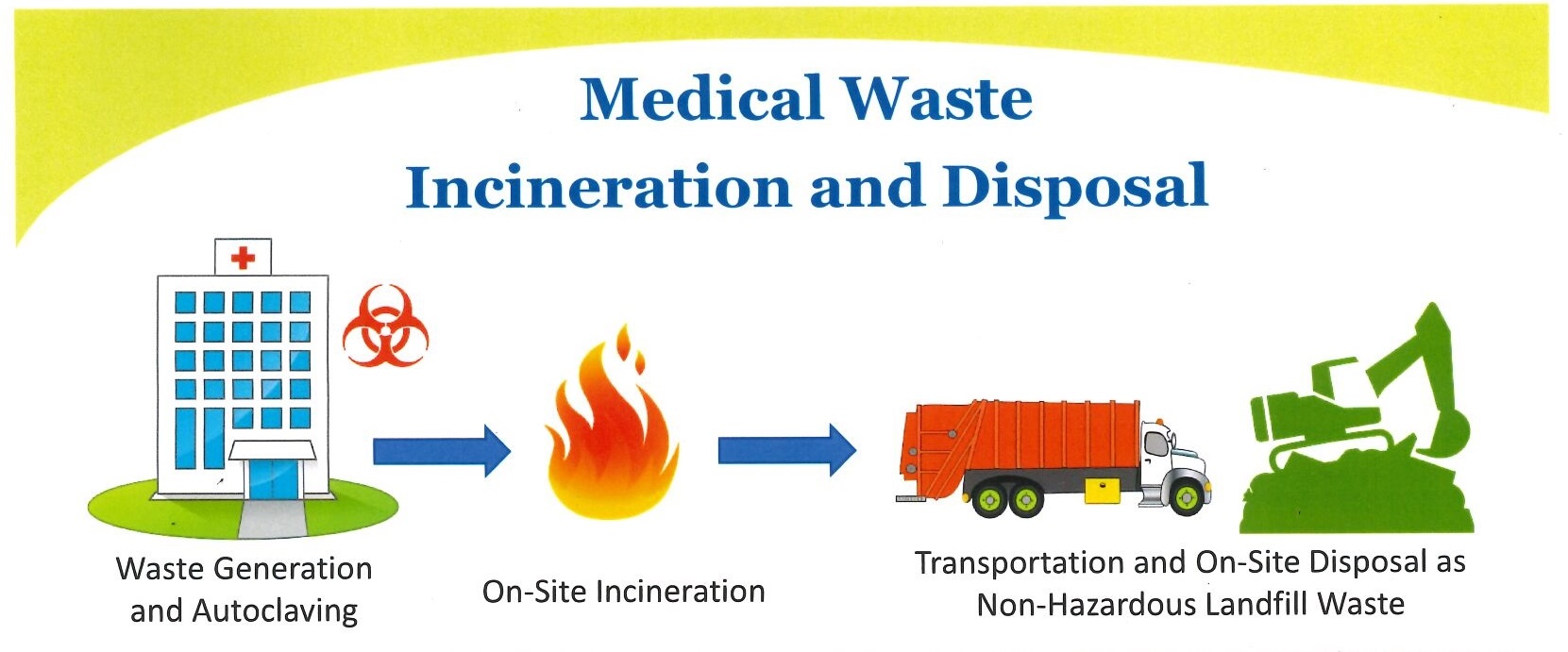
Medical waste disposal is critical to healthcare management particularly when it involves anatomical waste This type of waste includes human tissues organs and body parts that require specialized handling and disposal procedures to ensure safety and compliance with health regulations Proper disposal is essential to prevent potential health risks and environmental contamination Implementing effective protocols for the disposal of anatomical waste protects public health and aligns with legal and ethical responsibilities within the healthcare sector
Disposal of Anatomical Waste:
- Incineration: Incineration is recognized as the most common and effective method for disposing of anatomical waste. This process involves burning the waste at high temperatures, which ensures the destruction of pathogens and minimizes environmental impact.
- Alternative Methods: Depending on the type of waste and local regulations, other disposal methods may include chemical treatment (which involves using chemicals to neutralize waste), autoclaving (a sterilization process using steam and pressure), or burial in designated landfill sites that meet specific regulatory standards.
- Proper Segregation and Packaging: Anatomical waste must be carefully segregated from other types of waste to facilitate safe disposal. It should be placed in designated containers, which are often color-coded red to indicate the presence of hazardous materials. These containers should be clearly labeled to prevent confusion and ensure safe handling.
Compliance with Regulations:
The disposal of anatomical waste is subject to strict federal, state, and local regulations. Healthcare facilities must comply with these regulations to prevent the spread of infections and protect public health and the environment. Failure to adhere to these guidelines can result in severe penalties and risks to community safety.
According to guidelines from organizations like Business Waste Management, understanding the complexities of anatomical waste is crucial for healthcare professionals and waste management providers.
In conclusion
Now that you have a more comprehensive understanding of anatomical waste disposal, don’t hesitate to contact Secure Waste.
We provide reliable, compliant, eco-friendly medical waste disposal solutions for your facility’s needs. We have expertise in biomedical, hazardous waste, and Sharps container disposal. In addition, we provide customized waste management plans, including secure collection and transport, and sustainable disposal practices.
Contact us today for a FREE Waste Assessment, or request a quote online!
**Disclaimer** This information is provided for reference purposes only and should not be considered as legal advice or factual information at the time of your reading. Regulations frequently change and can vary from state to state. We encourage you to contact your local regulatory authorities or Secure Waste directly for the most current information. Please note that Secure Waste is not liable, in part or in whole, for any information contained on this page or website.

Expert Medical Waste Management: With over 25 years of industry experience, Secure Waste is a trusted local leader in hazardous and biohazardous waste disposal across Maryland, Virginia, and Washington, D.C. Specializing in medical waste management, sharps needle disposal, and biohazard waste removal, the company ensures full compliance with federal, state, and local regulations while prioritizing environmental sustainability.
The company also offers additional services, including secure document shredding and sharps container sales, providing comprehensive solutions for healthcare facilities and businesses. Our cost-effective services help clients maintain regulatory compliance without unexpected costs.
With a commitment to customer satisfaction, Secure Waste offers tailored waste management plans that align with industry best practices. Their team of experts provides reliable, timely, and compliant services, making them the preferred choice for medical waste disposal. For a free waste quote or more information, visit www.securewaste.net