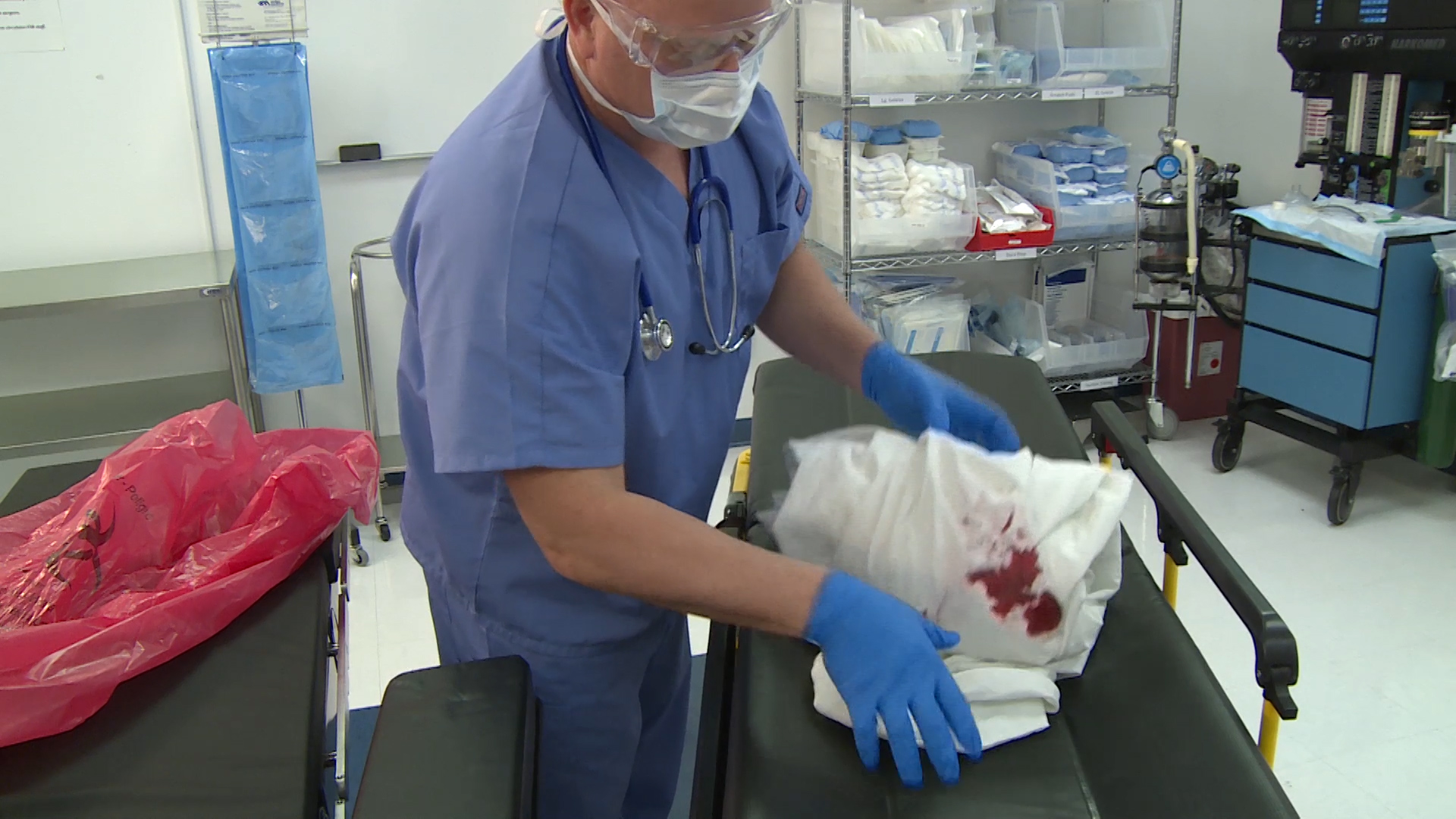
Secure Medical Waste Disposal for PHI and HIPAA Compliance
Proper disposal of medical waste is crucial for safeguarding patient privacy and ensuring compliance in healthcare facilities of all sizes. Any materials containing Protected Health Information (PHI) must be securely handled to comply with HIPAA regulations, as outlined by the HHS and documented by industry sources, such as the HIPAA Journal. This includes everything from paper records and prescription labels to electronic devices and imaging films that contain patient data.
Lapses in HIPAA compliance during waste disposal can lead to serious data breaches and substantial financial penalties, potentially weakening healthcare organizations. The consequences extend beyond monetary fines. Organizations face reputational damage, loss of patient trust, and mandatory corrective action plans that require significant resources to implement. For example, OCR enforcement actions have resulted in over $144 million in penalties for HIPAA violations as of 2024, demonstrating the government’s commitment to protecting patient privacy at every stage of the healthcare process.
Secure medical waste removal ensures that discarded records, devices, or any materials containing sensitive information cannot be retrieved by unauthorized parties, whether malicious actors, identity thieves, or simply curious individuals. This protection safeguards both patients and the healthcare organization from the devastating consequences of data breaches. In an era where healthcare data is increasingly valuable on the black market, proper disposal procedures serve as the final line of defense in protecting patient privacy.

HIPAA Compliance in Medical Waste Disposal
The HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules require healthcare organizations to apply comprehensive administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to PHI, even when disposing of it at the end of its lifecycle. This requirement recognizes that patient data remains sensitive and valuable regardless of whether it is actively being used for treatment or has been designated for disposal.
Covered entities must not simply discard PHI into a public-accessible dumpster. This may seem obvious, but violations of this fundamental principle persist, often resulting in significant penalties. The rules are clear: unsecured disposal of patient information is a direct violation of HIPAA requirements and exposes organizations to both regulatory action and civil liability.
When health information is no longer needed for its intended purpose, HIPAA mandates that it be permanently destroyed so it cannot be reconstructed by any means. This destruction must be thorough and complete, rendering the information completely unreadable and beyond recovery. Half measures or inadequate destruction methods leave organizations vulnerable to data breaches and compliance violations.
Standard destruction methods include cross-cut shredding of paper records, which cuts documents in multiple directions to prevent reconstruction, and degaussing or physically destroying electronic media such as hard drives, USB drives, and backup tapes. For electronic devices, simply deleting files is insufficient. Data must be rendered permanently inaccessible through approved methods, such as degaussing, which uses magnetic fields to erase data, or physical destruction, including crushing, shredding, or incinerating the storage media.
Organizations should document these procedures as part of their comprehensive HIPAA compliance program. Documentation serves multiple purposes: it demonstrates due diligence, provides evidence of compliance during audits, and establishes clear protocols for staff to follow. Policies should specify the types of waste that contain PHI, how it should be segregated, the approved destruction methods, and who is responsible for overseeing the disposal process.
Failing to implement reasonable disposal safeguards can result in costly penalties and corrective action plans mandated by regulatory authorities. The Office for Civil Rights actively investigates disposal-related breaches and has imposed substantial fines on organizations that fail to destroy PHI properly. Beyond financial penalties, organizations may be required to implement extensive corrective measures, undergo monitoring, and provide detailed compliance reports for years following a violation.
OSHA Compliance and Healthcare Worker Safety
Healthcare waste often includes sharps, such as needles and scalpels, as well as infectious materials that pose serious health risks; therefore, OSHA compliance is also critical for any medical facility. While HIPAA focuses on patient privacy, OSHA regulations protect the healthcare workers who handle potentially dangerous waste every day.
The OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard (29 CFR 1910.1030) mandates comprehensive training programs and engineering controls to minimize needlestick injuries and exposure risks to infectious diseases. Healthcare facilities must implement specific safeguards, including the use of puncture-resistant sharps containers, self-sheathing needles where appropriate, and proper handling protocols that minimize worker contact with contaminated materials.
Facilities should thoroughly train staff on the safe handling of contaminated waste, as recommended by OSHA and documented in compliance resources such as Stericycle. This training must be provided at the time of hire, annually thereafter, and whenever procedures change. Workers need to understand the types of waste they may encounter, the risks associated with each category, the proper use of personal protective equipment, and emergency procedures in the event of exposure.
Proper segregation of waste is essential for both safety and compliance. This includes using puncture-resistant sharps containers that are clearly marked and easily accessible, as well as color-coded bags for different waste streams (red bags for biohazardous waste, yellow bags for chemotherapy waste, etc.). Additionally, rigid containers are used for pathological waste. Each type of waste requires specific handling procedures to protect workers and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Timely disposal of biohazardous waste protects both workers and patients by preventing accumulation of infectious materials, reducing odors, and minimizing the risk of container overflow or rupture. Waste should not be allowed to accumulate beyond regulatory time limits or storage capacity. By adhering to OSHA guidelines, healthcare organizations maintain a safer workplace and significantly reduce accidents related to medical waste handling.
Best Practices for Secure Waste Removal
Healthcare providers should adopt clear, written procedures to ensure that PHI and hazardous waste are handled securely and in compliance with all applicable regulations. Follow these best practices to improve patient data protection and operational safety:
Segregate PHI-Containing Waste. Identify all documents, devices, and materials that include patient data from the moment they are designated for disposal. Store them in locked, clearly labeled containers until destruction can be completed. HIPAA guidance emphasizes that PHI must be managed under strict safeguards at all times, including the period between designation for disposal and actual destruction. Never mix PHI-containing waste with regular trash, as unauthorized individuals may have access to it.
Use Approved Destruction Methods. Shred, pulverize, or otherwise destroy PHI so it cannot be read or reconstructed through any reasonable means. For example, paper records should be cross-cut shredded into particles small enough to prevent reconstruction. Simple strip shredding is insufficient, as documents can be pieced back together. Media devices such as hard drives, smartphones, and tablets should be degaussed to erase magnetic data or physically destroyed through crushing or shredding to render them completely unusable.
Partner with Certified Vendors. Hire a HIPAA-compliant, secure waste removal service for pickup and destruction of regulated waste. Not all waste disposal companies are equipped to handle PHI or medical waste properly. Please ensure that contracts require the vendor to protect PHI and comply with HIPAA and OSHA requirements. Request proof of certifications, insurance, and compliance with relevant regulations. A Business Associate Agreement (BAA) is required when a vendor will have access to PHI, even if that access is only for destruction purposes.
Document the Process. Maintain certificates of destruction and detailed logs of waste pickups for all PHI disposal activities. Proper documentation demonstrates compliance and can help protect against liability in the event of an audit or regulatory investigation. Records should include dates, types of materials destroyed, methods used, witnesses present, and the names of vendors involved. Keep these records for the duration required by your state’s regulations, typically at least six years.
Train Your Staff. Provide comprehensive training on disposal policies and OSHA safety measures to all employees who handle medical waste, ensuring they are well-informed and equipped to handle these responsibilities effectively. OSHA requires healthcare employers to train workers on the risks and prevention strategies of bloodborne pathogens, which include proper waste handling procedures from generation through final disposal. Training should be hands-on and include demonstrations of appropriate techniques to ensure effective learning. Please ensure that you document all training sessions and maintain accurate records of employee attendance and comprehension.
Review and Audit Regularly. Conduct periodic audits of your waste management process to identify gaps and ensure ongoing compliance with regulations. Verify that containers are used appropriately, PHI is disposed of correctly, safety equipment is available and functioning, and protocols are consistently followed. Updating policies and training based on audit findings ensures continuous compliance with HIPAA and OSHA regulations. Schedule audits at least annually, and consider more frequent reviews if you have had compliance issues or significant staff turnover.
Expert Tip: Make compliance reviews an integral part of your routine operations, rather than treating them as isolated events. HHS emphasizes the importance of implementing “reasonable safeguards” during the disposal of PHI, so regularly reviewing your waste handling process can prevent costly violations before they occur. Assign responsibility for waste compliance to specific individuals and include it in performance evaluations to ensure accountability.
Sustainable Waste Practices in Healthcare
An effective healthcare waste management program also considers environmental impact and sustainability alongside regulatory compliance. Hospitals generate over 5 million tons of waste annually, equivalent to approximately 29 pounds per bed per day. This enormous volume has significant environmental implications, from landfill usage to greenhouse gas emissions from incineration.
Wherever possible, segregate recyclable materials, such as clean paper, cardboard, plastics, and metals, from regulated waste to support recycling initiatives. Many items that end up in red bags marked for incineration could actually be recycled if segregated adequately at the point of use. Educating staff about what can and cannot be recycled, and providing convenient recycling containers throughout the facility, can dramatically reduce the volume of waste requiring special handling and disposal.
The World Health Organization recommends prioritizing waste minimization through green procurement policies, the use of reusable supplies where safe and appropriate, and careful ordering practices to reduce excess supplies that may expire and require disposal. For example, rather than opening entire surgical kits when only a few instruments are needed, consider custom-packing procedures. Implement inventory management systems that utilize the first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle to minimize the expiration of medications and supplies.
Steam sterilization (autoclaving) and properly managed disinfection can treat specific waste streams without incineration, significantly reducing emissions and environmental impact. Many facilities have successfully implemented on-site autoclaving systems that render infectious waste non-hazardous, allowing it to be disposed of as regular solid waste. This approach reduces both environmental impact and disposal costs while maintaining safety and compliance.
Healthcare organizations can also explore innovative waste-to-energy technologies, composting of appropriate organic waste, and partnerships with specialized recyclers who can handle items like blue wrap, batteries, and electronic equipment. By integrating sustainable practices into medical waste disposal, healthcare facilities can protect patient data, ensure worker safety, and benefit the planet simultaneously.
Effective medical waste disposal is a cornerstone of both patient privacy and workplace safety in modern healthcare. By following HIPAA rules for the secure destruction of PHI, as mandated by HHS and documented in resources such as the HIPAA Journal, and OSHA protocols for handling biohazards, as outlined by compliance authorities like Stericycle, healthcare organizations can safeguard both sensitive patient information and employee health simultaneously.
The integration of sustainable waste management practices adds significant value by reducing environmental impact without compromising safety or compliance. As healthcare continues to evolve, waste management strategies must adapt to address new types of data storage, emerging pathogens, and increasing environmental awareness.
For more information or assistance with implementing compliant medical waste disposal procedures, please get in touch with Secure Waste. Their secure waste removal solutions help healthcare providers meet all regulatory requirements while safely disposing of sensitive materials, protecting patients, staff, and the environment.
In Conclusion:
Now that you have a more comprehensive understanding of PHI, don’t hesitate to contact Secure Waste.
We provide reliable, compliant, and environmentally friendly medical waste disposal solutions tailored to your facility’s specific needs. We have expertise in biomedical waste, hazardous waste, and Sharps container disposal. Additionally, we offer customized waste management plans, including secure collection and transportation, as well as sustainable disposal practices.
**Disclaimer** This information is provided for reference purposes only and should not be considered as legal advice or factual information at the time of your reading. Regulations frequently change and can vary from state to state. We encourage you to contact your local regulatory authorities or Secure Waste directly for the most current information. Please note that Secure Waste is not liable, in part or in whole, for any information contained on this page or website.

Expert Medical Waste Management: With over 25 years of industry experience, Secure Waste is a trusted local leader in hazardous and biohazardous waste disposal across Maryland, Virginia, and Washington, D.C. Specializing in medical waste management, sharps needle disposal, and biohazard waste removal, the company ensures full compliance with federal, state, and local regulations while prioritizing environmental sustainability.
The company also offers additional services, including secure document shredding and sharps container sales, providing comprehensive solutions for healthcare facilities and businesses. Our cost-effective services help clients maintain regulatory compliance without unexpected costs.
With a commitment to customer satisfaction, Secure Waste offers tailored waste management plans that align with industry best practices. Their team of experts provides reliable, timely, and compliant services, making them the preferred choice for medical waste disposal. For a free waste quote or more information, visit www.securewaste.net