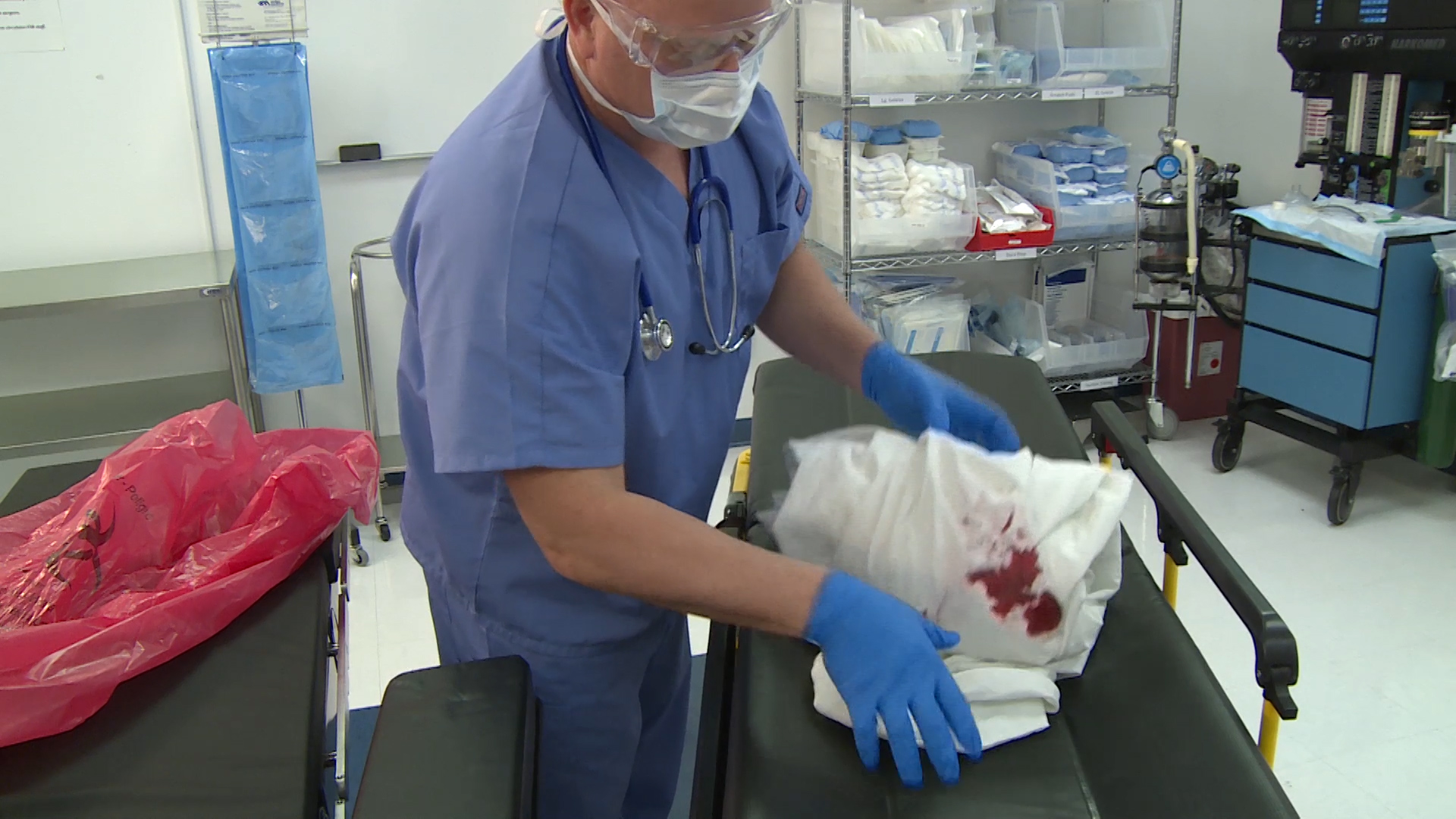
Managing Pathological Waste in Healthcare Facilities: What Are The Challenges? Expert Solutions From Secure Waste, an Industry Leader in Waste Disposal
Pathological waste poses challenges that are far more complex than those associated with general medical waste. While medical waste includes items such as syringes, bandages, and disposable materials, pathological waste consists of human tissues, organs, and anatomical materials that require stricter control, deeper risk assessment, and more specialized handling. Its sensitive biological nature makes the handling process more complex, leaving healthcare facilities vulnerable to compliance issues and operational risks if systems are not airtight. These added layers of responsibility make pathological waste a uniquely challenging category within healthcare waste streams.
This post will examine the complexities of pathological waste management, from the regulatory landscape to the common challenges faced by facilities. We will discuss the severe impacts of mismanagement and provide clear, actionable strategies for effective and compliant disposal. Without any delay, let’s get straight into it!
Regulatory Framework and Compliance Importance
In the United States, several key agencies and laws dictate how healthcare facilities must manage this waste stream. Here is the list:
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration):
Ensures healthcare workers’ safety when handling blood and OPIM. Requires PPE, engineering controls such as puncture-resistant containers, and training to prevent exposure to infectious and pathological waste.
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency):
Guides safe treatment and disposal of pathological waste. Sets standards for incineration and other methods to minimize environmental contamination, ensuring compliance with federal safety and environmental requirements.
DOT (Department of Transportation):
Regulates the transportation of pathological waste. Mandates proper packaging, labeling, and shipping procedures to prevent spills, leaks, or exposure during transit from healthcare facilities to certified disposal sites.
State and Local Regulations:
Often stricter than federal rules. Cover storage limits, segregation, approved treatment methods, and record-keeping. For example, regulations for sharps disposal in Virginia differ from those in other states, requiring adherence to local guidelines for container use, labeling, and disposal.
What are the Common Challenges in Pathological Waste Management
Hospitals and other healthcare facilities face several persistent challenges in managing their pathological waste streams effectively. These challenges include the following:
Proper Segregation at the Point of Generation
One of the most significant hurdles is ensuring correct waste segregation. Pathological waste must be separated from other waste streams, such as general trash, sharps, and pharmaceutical waste, at the moment it is generated. Errors in segregation can lead to cross-contamination, increased disposal costs (as less hazardous waste gets treated as pathological waste), and regulatory fines. Staff training and clear, color-coded container systems are crucial, but high-pressure clinical environments can lead to mistakes.
Safe Storage and Handling
Pathological waste requires specific storage conditions. It must be kept in leak-proof containers and often needs refrigeration to prevent decomposition and odor, especially if it cannot be collected for disposal immediately. Facilities must allocate dedicated, secure storage areas that are inaccessible to unauthorized personnel. Limited space, particularly in smaller clinics or older hospitals, can make it challenging to meet these storage requirements.
Complex Transportation Logistics
Transporting pathological waste from the healthcare facility to a treatment site is a highly regulated process. Challenges include finding a certified medical waste hauler, ensuring all waste is correctly packaged and labeled according to DOT standards, and completing the necessary shipping manifests accurately. Any misstep in this chain of custody can result in penalties and public health risks.
Limited Treatment and Disposal Options
The accepted methods for treating pathological waste, primarily incineration, are limited and face increasing environmental scrutiny. Incinerators are expensive to operate and must comply with strict air quality standards. Other technologies, like chemical disinfection or autoclaving, may not be suitable for all types of pathological waste or extensive anatomical parts. This scarcity of disposal options can drive up costs and create logistical bottlenecks for healthcare providers.
High Costs of Compliance
Effective pathological waste management is expensive. Costs include specialized containers, PPE for staff, extensive and ongoing training programs, licensed transportation services, and high fees for treatment and disposal. For many healthcare facilities, especially those with tight budgets, these costs represent a significant financial burden, sometimes leading to shortcuts that compromise safety and compliance.
What is the Impact of Mismanagement
The consequences of failing to manage pathological waste properly are far-reaching and severe.
- Public Health Risks: Improperly disposed of pathological waste can contaminate soil and water, potentially spreading infectious agents like bacteria and viruses into the community.
- Occupational Hazards: Healthcare workers, janitorial staff, and waste handlers are at high risk of needle-stick injuries and exposure to pathogens if waste is not segregated and contained correctly.
- Legal and Financial Penalties: Non-compliance with regulations can lead to substantial fines, loss of licensure, and costly litigation. A facility’s public image can also be irreparably damaged, leading to a loss of patient trust.
- Environmental Damage: Certain treatment methods, like outdated incineration practices, can release harmful pollutants and dioxins into the atmosphere. Improper landfilling can lead to long-term environmental contamination.
How to Effectively Manage Pathological Waste
1. Develop a Comprehensive Waste Management Plan
Every healthcare facility should have a detailed plan that outlines the procedures for every step of the waste management process. This plan should cover:
- Segregation: Clear guidelines on how to separate pathological waste from other waste streams at the source.
- Containment: Specifications for the types of containers to be used—they must be leak-proof, puncture-resistant, and correctly labeled.
- Storage: Protocols for secure, refrigerated storage areas, including temperature logs and access control.
- Transportation: Procedures for safe on-site transport and criteria for selecting a certified medical waste disposal partner.
2. Implement Staff Training Programs
Training should be mandatory for all employees who may come into contact with pathological waste. This includes not only clinical staff but also support and custodial teams. Training should be conducted upon hiring and refreshed annually or whenever regulations change. Practical training ensures that everyone understands their role and the importance of following established protocols.
3. Partner with a Certified Disposal Vendor
Choosing the right medical waste disposal partner is one of the most critical decisions a facility can make. A reputable vendor will not only handle the transportation and treatment of waste but also guide compliance and best practices. They should offer a manifest or tracking system that documents the waste from collection to final destruction, providing a transparent chain of custody for regulatory purposes.
4. Conduct Regular Audits
I’d like to emphasize that regularly auditing your waste management practices is crucial for identifying gaps and areas for improvement. Audits can help you track waste generation rates, verify compliance with segregation and labeling rules, and ensure that your disposal vendor is meeting its contractual obligations. These audits provide the data needed to refine your processes and reduce risks.
Securing Your Facility’s Safety and Compliance
Effectively managing pathological waste is a fundamental responsibility for any healthcare facility. By developing a comprehensive management plan, investing in continuous staff training, partnering with certified disposal experts, and conducting regular audits, organizations can navigate the complexities of this critical task. A proactive approach to pathological waste management not only ensures regulatory compliance but also protects the health and safety of staff, patients, and the community, reinforcing the facility’s commitment to excellence in care.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should pathological waste be collected and disposed of?
Pathological waste should be collected frequently, ideally on a daily basis or whenever containers reach capacity, to prevent decomposition, odors, and contamination. Regular collection is essential for effective pathological waste management and compliance with medical waste management standards.
Why does pathological waste require incineration?
Incineration is often the required treatment method because it ensures the destruction of all biological material, eliminating any potential pathogens. This high-temperature process reduces the waste to ash, rendering it sterile and non-infectious. Some states may allow for alternative treatments, but incineration remains the most common and effective method.
How can our facility reduce the cost of pathological waste disposal?
The most effective way to reduce costs is through proper waste segregation. By ensuring that only actual pathological waste is placed in designated containers, you avoid paying the higher disposal fees for items that could be managed as regular medical waste or even general trash. Training staff on proper segregation practices is crucial to achieving this goal.
Can pathological waste be treated on-site?
Some facilities with proper equipment, such as autoclaves or incinerators, can treat certain types of pathological waste on-site. However, many facilities rely on certified medical waste disposal vendors for safe and compliant treatment.

Expert Medical Waste Management: With over 25 years of industry experience, Secure Waste is a trusted local leader in hazardous and biohazardous waste disposal across Maryland, Virginia, and Washington, D.C. Specializing in medical waste management, sharps needle disposal, and biohazard waste removal, the company ensures full compliance with federal, state, and local regulations while prioritizing environmental sustainability.
The company also offers additional services, including secure document shredding and sharps container sales, providing comprehensive solutions for healthcare facilities and businesses. Our cost-effective services help clients maintain regulatory compliance without unexpected costs.
With a commitment to customer satisfaction, Secure Waste offers tailored waste management plans that align with industry best practices. Their team of experts provides reliable, timely, and compliant services, making them the preferred choice for medical waste disposal. For a free waste quote or more information, visit www.securewaste.net